import numpy as np
import scipy.sparse as sp
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import scipy.sparse.linalg as slinalg
class BrunaGraphConv(nn.Module):
"""
Bruna's Spectral Graph Convolution Layer
This implementation follows the original formulation by Joan Bruna et al.,
using the eigendecomposition of the graph Laplacian for spectral convolution.
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, n_nodes):
"""
Initialize the Bruna Graph Convolution layer
Args:
in_features (int): Number of input features
out_features (int): Number of output features
"""
super(BrunaGraphConv, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
# Learnable spectral filter parameters
self.weight = nn.Parameter(
torch.FloatTensor(in_features, out_features, n_nodes-1)
)
# Initialize parameters
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
"""Initialize weights using Glorot initialization"""
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
@staticmethod
def get_laplacian_eigenvectors(adj):
"""
Compute eigendecomposition of the normalized graph Laplacian
Args:
adj: Adjacency matrix
Returns:
eigenvalues, eigenvectors of the normalized Laplacian
"""
# Compute normalized Laplacian
# Add self-loops
adj = adj + sp.eye(adj.shape[0])
# Compute degree matrix
deg = np.array(adj.sum(axis=1))
Dsqrt_inv = sp.diags(1.0 / np.sqrt(deg).flatten())
# Compute normalized Laplacian: D^(-1/2) A D^(-1/2)
laplacian = sp.eye(adj.shape[0]) - Dsqrt_inv @ adj @ Dsqrt_inv
# Compute eigendecomposition
# Using k=adj.shape[0]-1 to get all non-zero eigenvalues
eigenvals, eigenvecs = slinalg.eigsh(laplacian.tocsc(), k=adj.shape[0]-1,which='SM', tol=1e-6)
return torch.FloatTensor(eigenvals), torch.FloatTensor(eigenvecs)
def forward(self, x, eigenvecs):
"""
Forward pass implementing Bruna's spectral convolution
Args:
x: Input features [num_nodes, in_features]
eigenvecs: Eigenvectors of the graph Laplacian [num_nodes, num_nodes-1]
Returns:
Output features [num_nodes, out_features]
"""
# Transform to spectral domain
x_spectral = torch.matmul(eigenvecs.t(), x) # [num_nodes-1, in_features]
# Initialize output tensor
out = torch.zeros(x.size(0), self.out_features, device=x.device)
# For each input-output feature pair
for i in range(self.in_features):
for j in range(self.out_features):
# Element-wise multiplication in spectral domain
# This is the actual spectral filtering operation
filtered = x_spectral[:, i] * self.weight[i, j, :] # [num_spectrum]
# Transform back to spatial domain and accumulate
out[:, j] += torch.matmul(eigenvecs, filtered)
return outAppendix: Graph Neural Networks
1 Bruna’s Spectral GCN
Let’s first implement Bruna’s spectral GCN.
Next, we will train the model on the karate club network to predict the given node labels indicating nodes’ community memberships. We load the data by
import networkx as nx
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load karate club network
G = nx.karate_club_graph()
adj = nx.to_scipy_sparse_array(G)
features = torch.eye(G.number_of_nodes())
labels = torch.tensor([G.nodes[i]['club'] == 'Officer' for i in G.nodes()], dtype=torch.long)We apply the convolution twice with ReLu activation in between. This can be implemented by preparing two independent BrunaGraphConv layers, applying them consecutively, and adding a ReLu activation in between.
# Define a simple GCN model
class SimpleGCN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, hidden_features, n_nodes):
super(SimpleGCN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = BrunaGraphConv(in_features, hidden_features, n_nodes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = BrunaGraphConv(hidden_features, out_features, n_nodes)
def forward(self, x, eigenvecs):
x = self.conv1(x, eigenvecs)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.conv2(x, eigenvecs)
return xWe then train the model by
import torch.optim as optim
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Get eigenvectors of the Laplacian
eigenvals, eigenvecs = BrunaGraphConv.get_laplacian_eigenvectors(adj)
# Initialize the model
hidden_features = 10
input_features = features.shape[1]
output_features = 2
n_nodes = G.number_of_nodes()
model = SimpleGCN(input_features, output_features, hidden_features, n_nodes)
# Train the model
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Split the data into training and testing sets
train_idx, test_idx = train_test_split(np.arange(G.number_of_nodes()), test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
train_features = features[train_idx]
train_labels = labels[train_idx]
test_features = features[test_idx]
test_labels = labels[test_idx]
n_train = 100
for epoch in range(n_train):
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(train_features, eigenvecs[train_idx, :])
loss = criterion(output, train_labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Evaluate the model
if epoch == 0 or (epoch+1) % 25 == 0:
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(test_features, eigenvecs[test_idx, :])
_, predicted = torch.max(output, 1)
accuracy = (predicted == test_labels).float().mean()
print(f'Epoch {epoch+1}/{n_train}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}, Accuracy: {accuracy.item():.4f}')Epoch 1/100, Loss: 0.6940, Accuracy: 0.2857
Epoch 25/100, Loss: 0.1436, Accuracy: 0.2857
Epoch 50/100, Loss: 0.0052, Accuracy: 0.4286
Epoch 75/100, Loss: 0.0019, Accuracy: 0.4286
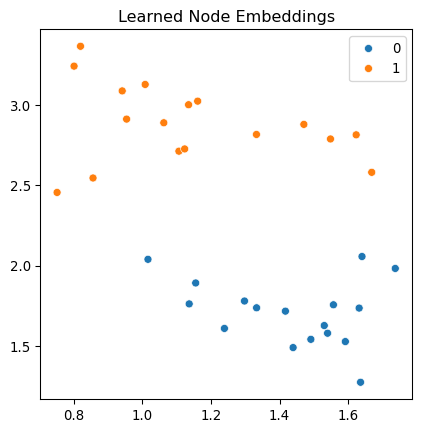
Epoch 100/100, Loss: 0.0013, Accuracy: 0.4286Observe that the accuracy increases as the training progresses. We can use the model to predict the labels. The model has a hidden layer, and let’s visualize the data in the hidden space.
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
# Visualize the learned embeddings
embeddings = model.conv1(features, eigenvecs).detach().numpy()
xy = TSNE(n_components=2).fit_transform(embeddings)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 5))
sns.scatterplot(x = xy[:, 0].reshape(-1), y = xy[:, 1].reshape(-1), hue=labels.numpy(), palette='tab10', ax = ax)
ax.set_title("Learned Node Embeddings")
plt.show()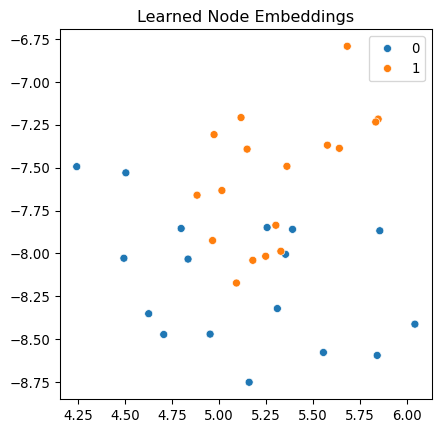
2 ChebNet
Let’s implement the ChebNet layer.
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import scipy.sparse as sp
from typing import Optional
def sparse_mx_to_torch_sparse(sparse_mx):
"""Convert scipy sparse matrix to torch sparse tensor."""
sparse_mx = sparse_mx.tocoo()
indices = torch.from_numpy(
np.vstack((sparse_mx.row, sparse_mx.col)).astype(np.int64)
)
values = torch.from_numpy(sparse_mx.data.astype(np.float32))
shape = torch.Size(sparse_mx.shape)
return torch.sparse_coo_tensor(indices, values, shape)
class ChebConv(nn.Module):
"""
Chebyshev Spectral Graph Convolutional Layer
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels: int, out_channels: int, K: int, bias: bool = True):
super(ChebConv, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.K = K
# Trainable parameters
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(K, in_channels, out_channels))
if bias:
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_channels))
else:
self.register_parameter("bias", None)
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
"""Initialize parameters."""
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
if self.bias is not None:
nn.init.zeros_(self.bias)
def _normalize_laplacian(self, adj_matrix):
"""
Compute normalized Laplacian L = I - D^(-1/2)AD^(-1/2)
"""
# Convert to scipy if it's not already
if not sp.isspmatrix(adj_matrix):
adj_matrix = sp.csr_matrix(adj_matrix)
adj_matrix = adj_matrix.astype(float)
# Compute degree matrix D
rowsum = np.array(adj_matrix.sum(1)).flatten()
d_inv_sqrt = np.power(rowsum, -0.5)
d_inv_sqrt[np.isinf(d_inv_sqrt)] = 0.0
d_mat_inv_sqrt = sp.diags(d_inv_sqrt)
# Compute L = I - D^(-1/2)AD^(-1/2)
n = adj_matrix.shape[0]
L = sp.eye(n) - d_mat_inv_sqrt @ adj_matrix @ d_mat_inv_sqrt
return L
def _scale_laplacian(self, L):
"""
Scale Laplacian eigenvalues to [-1, 1] interval
L_scaled = 2L/lambda_max - I
"""
try:
# Compute largest eigenvalue
eigenval, _ = sp.linalg.eigsh(L, k=1, which="LM", return_eigenvectors=False)
lambda_max = eigenval[0]
except:
# Approximate lambda_max = 2 if eigenvalue computation fails
lambda_max = 2.0
n = L.shape[0]
L_scaled = (2.0 / lambda_max) * L - sp.eye(n)
return L_scaled
def chebyshev_basis(self, L_sparse: torch.sparse.Tensor, X: torch.Tensor):
"""
Compute Chebyshev polynomials basis up to order K.
"""
# List to store Chebyshev polynomials
cheb_polynomials = []
# T_0(L) = I
cheb_polynomials.append(X)
if self.K > 1:
# T_1(L) = L
X_1 = torch.sparse.mm(L_sparse, X)
cheb_polynomials.append(X_1)
# Recurrence T_k(L) = 2L·T_{k-1}(L) - T_{k-2}(L)
for k in range(2, self.K):
X_k = (
2 * torch.sparse.mm(L_sparse, cheb_polynomials[k - 1])
- cheb_polynomials[k - 2]
)
cheb_polynomials.append(X_k)
return torch.stack(cheb_polynomials, dim=0) # [K, num_nodes, in_channels]
def forward(self, X: torch.Tensor, adj_matrix: sp.spmatrix):
"""
Forward pass.
Args:
X: Node features tensor of shape [num_nodes, in_channels]
adj_matrix: Adjacency matrix in scipy sparse format
Returns:
Output tensor of shape [num_nodes, out_channels]
"""
# Compute normalized and scaled Laplacian
L_norm = self._normalize_laplacian(adj_matrix)
L_scaled = self._scale_laplacian(L_norm)
# Convert to torch sparse tensor
L_scaled = sparse_mx_to_torch_sparse(L_scaled).to(X.device)
# Compute Chebyshev polynomials basis
Tx = self.chebyshev_basis(L_scaled, X) # [K, num_nodes, in_channels]
# Perform convolution using learned weights
out = torch.einsum("kni,kio->no", Tx, self.weight)
if self.bias is not None:
out += self.bias
return outWe stack the layers to form a simple GCN model.
class ChebNet(nn.Module):
"""
ChebNet model for node classification
"""
def __init__(
self,
in_channels: int,
hidden_channels: int,
out_channels: int,
K: int,
num_layers: int,
dropout: float = 0.5,
):
super(ChebNet, self).__init__()
self.convs = nn.ModuleList()
# First layer
self.convs.append(ChebConv(in_channels, hidden_channels, K))
# Hidden layers
for _ in range(num_layers - 2):
self.convs.append(ChebConv(hidden_channels, hidden_channels, K))
# Output layer
self.convs.append(ChebConv(hidden_channels, out_channels, K))
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.activation = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, X: torch.Tensor, adj_matrix: sp.spmatrix):
"""
Forward pass through all layers
"""
for i, conv in enumerate(self.convs[:-1]):
X = conv(X, adj_matrix)
X = self.activation(X)
X = self.dropout(X)
# Output layer
X = self.convs[-1](X, adj_matrix)
return XLet’s train the model on the karate club network.
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
import networkx as nx
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load karate club network
G = nx.karate_club_graph()
adj = nx.to_scipy_sparse_array(G)
features = torch.eye(G.number_of_nodes())
labels = torch.tensor(
[G.nodes[i]["club"] == "Officer" for i in G.nodes()], dtype=torch.long
)
# Initialize the model
hidden_features = 10
input_features = features.shape[1]
output_features = 2
n_nodes = G.number_of_nodes()
K = 3
num_layers = 2
dropout = 0.5
model = ChebNet(
input_features, hidden_features, output_features, K, num_layers, dropout
)
import torch.optim as optim
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Train the model
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Split the data into training and testing sets
train_idx, test_idx = train_test_split(
np.arange(G.number_of_nodes()), test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
train_features = features[train_idx]
train_labels = labels[train_idx]
test_features = features[test_idx]
test_labels = labels[test_idx]
n_train = 100
for epoch in range(n_train):
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(features, adj)
loss = criterion(output[train_idx], train_labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Evaluate the model
if epoch == 0 or (epoch + 1) % 25 == 0:
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(features, adj)
_, predicted = torch.max(output[test_idx], 1)
accuracy = (predicted == test_labels).float().mean()
print(
f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{n_train}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}, Accuracy: {accuracy.item():.4f}"
)Epoch 1/100, Loss: 0.7328, Accuracy: 0.7143
Epoch 25/100, Loss: 0.1320, Accuracy: 0.8571
Epoch 50/100, Loss: 0.0149, Accuracy: 0.8571
Epoch 75/100, Loss: 0.0020, Accuracy: 0.8571
Epoch 100/100, Loss: 0.0054, Accuracy: 0.8571Let’s visualize the learned embeddings.
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# Get embeddings from the last hidden layer
X_hidden = features
for conv in model.convs[:-1]:
X_hidden = conv(X_hidden, adj)
X_hidden = model.activation(X_hidden)
# Reduce dimensionality for visualization
xy = TSNE(n_components=2).fit_transform(X_hidden.numpy())
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 5))
sns.scatterplot(
x=xy[:, 0].reshape(-1),
y=xy[:, 1].reshape(-1),
hue=labels.numpy(),
palette="tab10",
ax=ax,
)
ax.set_title("Learned Node Embeddings")
plt.show()