Embedding from Language Models (ELMo)#
ELMo is an embedding model that uses a deep, bidirectional LSTM architecture to generate word representations.
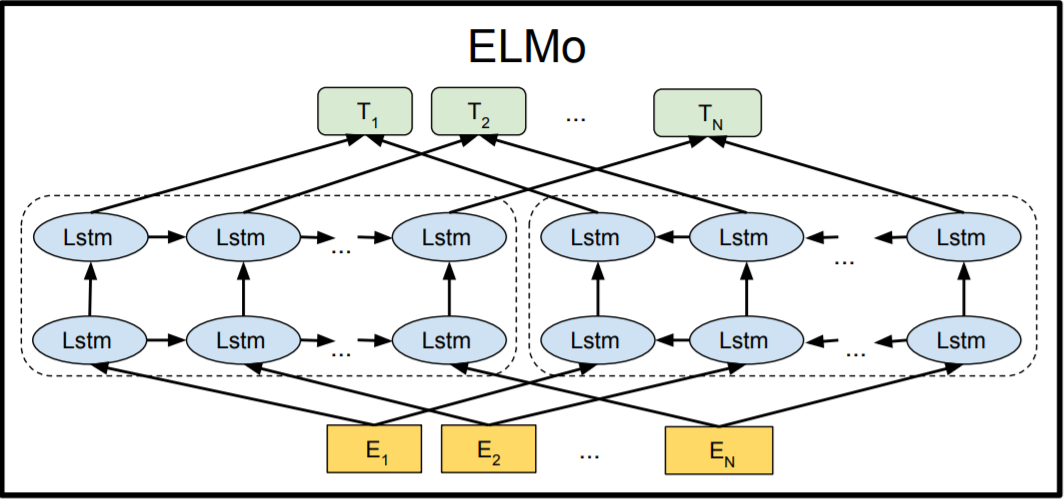
Fig. 11 ELMo architecture#
Overview#
ELMo consists of two main components, i.e., a character-level CNN and a bidirectional LSTM.
Character-level CNN#
Character-level CNN is a type of neural network architecture that processes text at the character level rather than the word level. This approach is particularly useful for handling out-of-vocabulary words, as it can process any sequence of characters, regardless of whether they form a valid word in the training set.
It is easy to understand it by considering an example of embedding a word “playing”. The word “playing” is generated from characters “p”, “l”, “a”, “y”, “i”, “n”, “g”. Each character is mapped to a learned embedding vector. The character embeddings are then convolved (i.e., weighted sum) with weights learned from data. The convolved output is then passed through a max-pooling layer that extracts the maximum value across the word length. This max-pooling operation creates a fixed-size word-level representation.
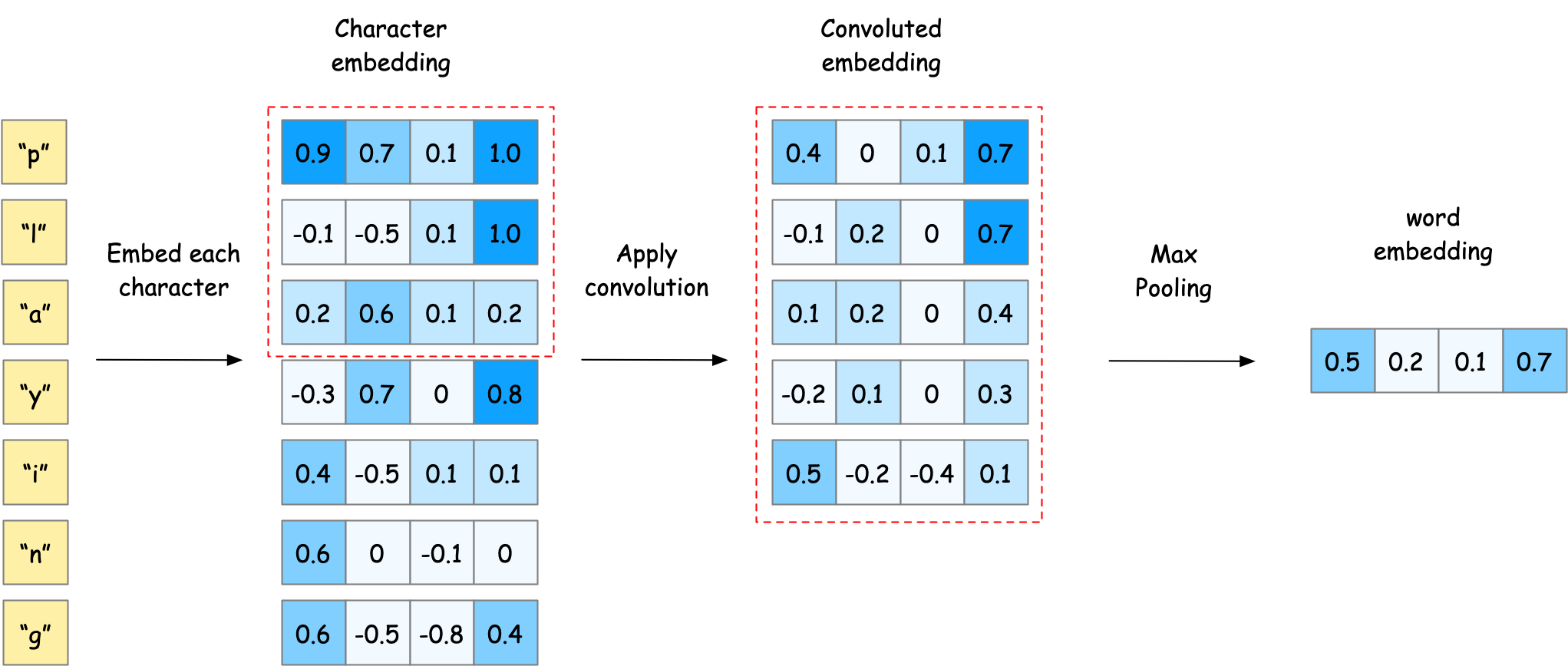
Fig. 12 Character-level CNN. Word “playing” is generated from characters “p”, “l”, “a”, “y”, “i”, “n”, “g”. Each character is mapped to a learned embedding vector, which is then convolved and max-pooled to create a fixed-size word-level representation.#
Bidirectional LSTM#
Bidirectional LSTM is a type of recurrent neural network that processes text in both forward and backward directions. Given a sequence of words, the forward LSTM processes the words from the first to the last, while the backward LSTM processes the words from the last to the first. The two LSTM outputs are then concatenated to form a single vector representation for each word.

Fig. 13 ELMo architecture#

